Goat Breeding Tips for Livestock Farmers (Urdu)
In order to get maximum meat and milk Beetal, Daira Deen Panah, Nachi, and Teddy Breeds.....
Mango Amazing Facts
The mango is known as the 'king of fruit' throughout the world. The name 'mango' is derived from the Tamil word 'mangkay' or 'man-gay'. When the Portuguese traders settled in Western India they adopted the name as 'manga'.
Pomegranate(Punica granatum) Cultivation and Farming
Pomegranates are fairly drought tolerant and can be grown on either calcareous or acid soils. Climate - Grow best in dry climates with mild winters. Chilling requirement
EU may also ban Monsanto GMO in wake of shocking cancer findings
Russia's consumer protection group, Rospotrebnadzor, said it was halting all imports of GM corn while the country's Institute of Nutrition will be evaluating the results of the study.
Protect Garden Pots during Winter
Many pots, especially ornamental containers that aren’t designed to stand outside in freezing temperatures, need winter protection. Wrap them up in burlap (possibly double layers), and secure tightly at the top and bottom with strong garden string.
Sustainable Agriculture and Fertilizers Practices in Pakistan
Agriculture is the mainstay of Pakistan’s economy. It has a total area of 79.61 million hectare, and the total area used for crop production is only 22 million ha.
Herbs For Winter Windowsill
Growing season is over, do you still find yourself ready to dash out to the garden for some chives, basil or a sprig of thyme...
Claim FREE EBook
Once you subscribe you will get a confirmation email from eagri about joining the mailing list.
Advertisement
Wednesday, May 01, 2013
Hydroponics for Home Gardeners
By: J. Raymond Kessler Jr., Extension Specialist, Associate Professor; J. David Williams, Department Head and former Extension Specialist; and Robyn Howe, Undergraduate Student, all in Horticulture, Auburn University

Hydroponics is, simply put, growing plants without soil. The discovery was made years ago that it was not the actual soil that plants need to grow is the mineral nutrients held by soil particles or those unleashed through the action of bacteria and worms. The nutrients slowly dissolve in the surrounding soil-water solution, and the roots then absorb the nutrients from the soil-water. All plants have the same basic needs whether they are grown in soil or not. When the plant’s nutritional needs are met, soil is no longer necessary. In fact, the soil may harbor pathogens and other organisms that could harm the plant. In hydroponics, all the nutrients are supplied in a water solution that passes over the roots or floods around them at regular intervals. Plants often grow faster in a hydroponic system because nutrients are immediately available and therefore can be assimilated faster.
When experimenting with hydroponics, as with all other gardening techniques, it is important that the gardener know the basic physiology of the plant that is, how the plant works. Plants use their roots to draw in water and minerals that are trans-ported upward into the leaves. They also take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide in respiration.
The leaves absorb energy during the day from sun-light and take up carbon dioxide from the air. The water from the roots, the carbon dioxide, and the light energy combine to form carbohydrates such as sugar. The plant then releases oxygen back into the atmosphere. These actions, aided by the nutrients gleaned from absorbed minerals, complete the process of photosynthesis, providing the energy and raw materials for growth. At night, the process reverses in the leaves. Carbohydrates break down, releasing the energy needed to create new leaves, stems, and roots, and carbon dioxide is released.

Substrate
In order to serve as a suitable replacement for soil, the substrate must be capable of supporting the root system and holding moisture and nutrients. It should be inert, free of insects and diseases, and not easily broken down. Also, the substrate should allow adequate aeration of the roots and have good drainage qualities. Plants need sufficient access to oxygen in the air in order to grow and take up water and nutrients. Poor drainage can lead to de-creased growth, stunting, wilting, and discoloration of the leaves and, in the worst cases, “drowning.” 
Several commonly used substrates are coarse sand (ask for washed river sand), gravel, perlite, coarse vermiculite, and rock wool. Perlite and coarse vermiculite are good choices because they are sterile, uniform, and readily available in garden centers. Sand and gravel also work well but should be washed thoroughly before planting to remove lime or other impurities.
Water
Mature plants process a surprisingly large amount of water. For instance, a fully grown to mato plant may use up to 2⁄3gallon of water a day. An inadequate water supply is the most limiting factor to plant growth. Water deficiencies can cause the plant to spend all its available energy on developing an extensive root system, the result being a small, stunted shoot. For this reason, it is important that the media be flooded, and subsequently drained, one to three times daily or as often as necessary to keep the roots moist.
Light
The amount of light required varies from plant to plant. Most fruiting plants such as corn, tomatoes, and peppers need 8 to 10 hours of sunlight a day. If these plants are grown indoors, an artificial light must be used to provide high light intensity without causing the temperature to rise above acceptable levels. This situation may be difficult to achieve. On the other hand, many ornamental and foliage plants require less sunlight than fruiting plants do and therefore perform very well indoors. One common error in applying hydroponics is trying to grow plants in reduced light when full sun is required.
Temperature

Nutrients
The key ingredient in the recipe for successful hydroponic gardening is the nutrient solution. In traditional soil-based gardening, the plant receives fertilizer from the slow breakdown of organic materials and the release of mineral nutrients in the soil. Hydroponic systems provide readily available, water-soluble minerals directly to the roots in a complete and balanced solution, thus eliminating the need for soil.
There are sixteen elements needed for plant growth. Plants extract several of these elements, such as oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen, from water and air. The rest of the elements must be supplied through the nutrient solution.
The primary macronutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). The secondary macro-nutrients are calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). These distinctions are made based on how much of each nutrient plants need. Micronutrients, or trace elements, such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and chlorine (Cl) are used in very small amounts by plants, hence the name micronutrients. Micronutrients are sometimes present as impurities in the water and in the solid substrate.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is central to the development of new leaves and stems as well as to overall growth and performance. An overabundance of nitrogen causes soft, weak growth and possible delay of fruit and flower production. Symptoms of nitrogen deficiency are yellowing leaves and weak, spindly growth.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is used by the plant in photosynthesis and in the production of flowers and seeds. It also encourages strong root growth. When phosphorus levels are low, the older leaves begin to turn deep green and develop brown or purple dis-coloration. Other symptoms may be stunted growth and chlorosis, or yellowing, of the lower leaves.
Potassium
Potassium is necessary during all stages of growth, particularly during fruit development. It is involved in the manufacture of sugars, starches, and chlorophyll. Potassium helps the plant make good use of air and water by regulating stomatal openings in the leaves and also helps build strong roots. Deficiency symptoms are mottling and yellowing of older leaves, generally along the margins, and flower and fruit drop. 
Calcium
Calcium is used by the plant in the manufacture and growth of cells. It also acts as a buffer for excess nutrients in soil. Calcium deficiency is recognizable by the curling and stunting of young leaves and dieback of the shoot tip. Too much calcium can stunt the growth of a young plant.
Magnesium
Magnesium is fundamental in the absorption of light energy and is central to the structure of the chlorophyll molecule. Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include curled leaf margins, yellowing of older leaves (veins remain green), and, eventually, bright green coloration of the growing tips.
Nutrient Solutions
The elements needed for successful hydroponic growth are widely available in premixed form from gardening catalogs, garden centers, fertilizer companies, and hydroponic supply companies. Most hydroponics amateurs will rely on these commercially available mixes rather than preparing their own solutions at home.
However, for those enthusiasts who are willing to mix their own, the extra time and effort may offer more precise nutrient combinations for specific plants, as well as provide an opportunity for experimentation. Many nutrient solution recipes have been developed, some for general use and others for specific plants, and no one recipe is better for all plants than another. Hydroponic nutrient solutions contain several water-soluble, nutritive salts that can be purchased at fertilizer companies, green-house supply companies, and chemical companies.
The primary and secondary macronutrient salts are usually mixed in a large volume of water at a concentration ready to use on plants. The micronutrients are mixed as separate concentrated solutions that are then added in a measured amount to the macronutrient solution.
To make your own solution, mix 10 gallons of macronutrient solution according to the recipe in either Table 1 or Table 2. Nutrient solution No. 1 is more appropriate for slow-growing plants and plants growing under low light intensity, such as foliage plants. Nutrient solution No. 2 is more appropriate for rapidly growing plants and plants under high light intensity, especially vegetables. Next, mix the following two micronutrient solutions, and add each to the macronutrient solution.
• Mix 7.6 grams (11⁄4level teaspoons) of boric acid (H3BO4) and 0.6 grams (1⁄10teaspoon) of manganese chloride (MnCl2• 4H2O) in 1 quart of water.
Use 1⁄2cup of this solution for 10 gallons of macro-nutrient solution.
• Mix 3 grams (1⁄2level teaspoon) of chelated iron (NaFe EDTA) in 1 quart of water. Use 1 3⁄5cup of this solution for 10 gallons of macronutrient solution.
After mixing the nutrient solutions together, check the pH. (Meters for measuring pH can be purchased from garden and hydroponic supply companies.) Most plants grow well in a slightly acidic solution with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5. If the solution is too alkaline (pH greater than 7.0), add a few drops of white vinegar per gallon, stir, and recheck the pH. If the solution is to acidic, add a small amount of baking soda per gallon to increase the pH. Continue rechecking and making adjustments until the desired pH level is reached.
The nutrient solution can be reused for 10 to 14 days when applied one to three times a day. At the end of this period, flood the substrate with clean water and drain it several times to wash out any accumulated materials. Mix and add a new solution.
Simple Hydroponic Systems
The simplest hydroponic system for beginners is a non recycling system consisting of a well-drained container filled with an acceptable A larger-scale version of the recycling method involves using a container that has a hose and an outlet an inch or two from its base. The container must be raised off the floor and tilted so that the nutrient solution drains through the outlet into a receptacle. These simple hand-fed methods work best with small-scale systems. For larger systems, a submersible pump can be used to pump the solution back into the container from the receptacle substrate. The nutrient solution is mixed, and then it is applied one to three times daily, using a simple watering can. The excess solution drains away and is lost.
A more economical technique is the recycling method, which involves collecting and reusing excess solution. The simplest version of this technique involves placing a large dish under the plant container to catch the solution and then pouring the solution back over the plant at regular intervals.
In addition to the systems that require a substrate, there are non aggregate methods such as water culture and aeroponics. In water culture, the plant’s roots are kept submerged in the nutrient solution. The plants are supported by a grid of wire, rope, or string or by coarse screening. This method, however, introduces aeration problems and re-quires an aquarium pump to bubble oxygen into the nutrient solution.
One simple version of water culture for a single plant consists of using a pint- to quart-sized glass or plastic bottle or jar that has a stopper or lid with two holes in it. The stem of a young plant is passed through one hole so that the plant is held above the nutrient solution and the roots are in the nutrient solution. The plant’s stem is surrounded with cotton for support. The nutrient solution is aerated by an aquarium pump. The plastic tube from the pump is passed through the second hole in the lid and into the nutrient solution. The container is covered with aluminum foil to keep light off the root system.
In aeroponics, the plant’s roots are suspended in air and are regularly misted with a fine spray of nutrient solution. Misting must occur often enough to cover the roots with a constant film of nutrient solution at all times. The misting chamber must be kept dark so algae does not grow and compete with the roots. This method requires more mechanical and electrical sophistication than the previous methods do. The methods that use a substrate are generally less expensive, are easier to transplant from, and have fewer difficulties than the water or aeroponics methods do.
Getting Started
It is important that the beginner keep in mind that hydroponics is not the perfect solution to all gardening woes. There are pros and cons to both traditional soil-based gardening and hydroponics. One major disadvantage of hydroponics is the commitment of time and energy necessary for success. Soilless gardening is much more exacting than traditional gardening and may overwhelm the novice gardener if too complex a system is implemented.
Begin with a small project such as an herb garden to get a feel for hydroponics, and, as your knowledge and comfort increase, move on to a more elaborate system.
Source: Alabama Cooperative Extension System
Cultural Methods of Vegetable Disease Control
Most vegetables are susceptible to one or more diseases. You can, therefore, anticipate disease problems sooner or later in your vegetable garden. By following good cultural practices and taking preventive measures, your chances of garden failure due to disease problems can be reduced.

Garden sites should not be within the drip line of large trees. Avoid planting near black walnut trees, since they produce a root sub-stance that is toxic to certain vegetables, especially tomatoes. The garden site should be slightly sloped to provide good water and air drainage through the soil.
Excess soil moisture can damage vegetable roots, as well as promote root diseases caused by certain fungi. Air movement through the garden is also important to help dry the foliage, thus reducing the chances of fungal and bacterial infections. Garden sites with good air drainage are less likely to be damaged by late frosts.
Most garden vegetables require full sunlight for maximum production. Sunlight also hastens drying of foliage. Soil tillage should be done early enough, prior to planting, to allow decomposition of raw organic matter such as manure or green plant material. This usually requires about six weeks under warm temperatures and longer at low temperatures. Organic material that has not decomposed can be a source of disease organisms and can also promote development of certain diseases such as root and stem rots. Applying nitrogen fertilizer before plowing or tilling green plant material into the soil will hasten its de-composition.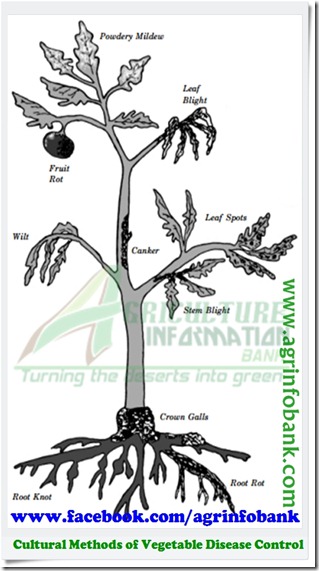
Crop rotation will help prevent the buildup of disease-causing organisms in the soil. Some disease causing organisms affect one vegetable or group of vegetables, but may not affect an-other. Several vegetables of the same family, such as squash, cucumbers and cantaloupes, may be affected by the same disease. Therefore, it is not a good practice to grow plants of the same family in rotation. Table 1 gives crop groupings for rotation to control soil-borne diseases. At least a three-year rotation is suggested for vegetable crops.
Sanitation is very important in controlling vegetable diseases. Many disease-causing organ-isms survive the winter in plant debris, cull fruit or plant stubble left in the garden. Any practice that will eliminate these overwintering sites for fungi, bacteria, viruses and nematodes will reduce the occurrence of disease problems the following year. Removal or plowing-under of crop stubble and trash helps destroy overwintering populations of disease organisms. Some disease-causing organisms are able to survive the off season on contaminated equipment or containers. Equipment that has been used in disease-infested vegetable gardens or containers used in handling diseased vegetables should be disinfested before being used again.
Disease-free seed and transplants are a must in vegetable production. Seed should not be saved from diseased plants. Always buy seed from a reputable dealer, since you normally cannot tell from their external appearance if seed are contaminated with disease-causing organisms.
Certain geographical areas, such as the arid western states, can produce disease-free seed because of climatic conditions. Seed from these areas should be stipulated in your seed orders. Gardeners starting their crop from transplants should, likewise, insist on disease-free plants.
Seed treatments vary, depending on the crop as well as the disease to be controlled. Some disease-causing organisms are carried on the surface of seed and can be controlled by a simple fungicide treatment. Fungicides are not effective against those organisms carried beneath the seed coat.
Fungicides applied to seed also give young seedlings some protection from soil-borne disease organisms as they germinate and emerge. Such treatments, however, do not control organisms that attack the plant after the seedling stage.
A seed treatment is usually applied by the company from which the seed is purchased. Home-grown seed can be treated at home with relative ease. Thiram or Captan fungicides can be used as seed treatments on most vegetable crops. Use these protectant fungicides according to instructions on the label. For small quantities of seed, such as packets, apply sufficient fungicide to coat the seed surface. Simply place a small quantity (comparable to the size of a match head) in the packet, reclose and shake to coat the seed with the fungicide.
Planting dates can be an effective tool in reducing diseases of vegetables. Okra, for in-stance, requires warm soil for good germination and growth. If planted when the soil is still cold, the seeds will rot, or if they do germinate, they will probably develop damping-off or stem rot. Some crops, such as corn and beans, should be planted as early as the weather permits to escape severe virus infections. Aphids that transmit viruses are usually at lower population levels early in the season.
Mulches can be used to conserve moisture, keep fruit clean and prevent diseases. Mulches reduce fruit rot on crops, such as strawberries, tomatoes, squash, cucumbers and melons by preventing direct contact with the soil. Mulching will reduce splashing of soil onto lower fruit and foliage by rain.
Staking or trellising tomatoes, pole or half runner beans and cucumbers will prevent soil contact with the foliage and fruit. Air circulation will be better if these plants are trellised, thus promoting better drying of foliage and reducing diseases. Pesticides can be more effectively applied to trellised plants.
Watering can influence the development and severity of many foliage diseases. Wet foliage is favorable for the development of most diseases. To reduce infections, apply irrigation water to the soil rather than the foliage. If water must be applied to the foliage, then it should be done in late morning or mid-afternoon to allow the foliage to dry before evening.
Maintaining uniform soil moisture can re-duce problems such as blossom end rot of pe-pers and tomatoes. Excessive soil moisture can result in increased root and stem rot diseases. It is best to work in the garden when the foliage is dry to reduce disease spread. Bacterial diseases of tomatoes, beans and other crops are readily spread on hands and clothing of workers when the foliage is wet.
Use of resistant varieties is one of the most economical ways of controlling vegetable diseases. Resistant varieties should be used in areas where diseases are present or where the soil is known to be infested with disease-causing organisms. Resistant varieties should be used even when rotation is practiced.

.jpg)



.jpg)










